Cucumber vs. zucchini – they’re both deceptively similar, but offer unique health benefits
04/16/2019 / By Zoey Sky
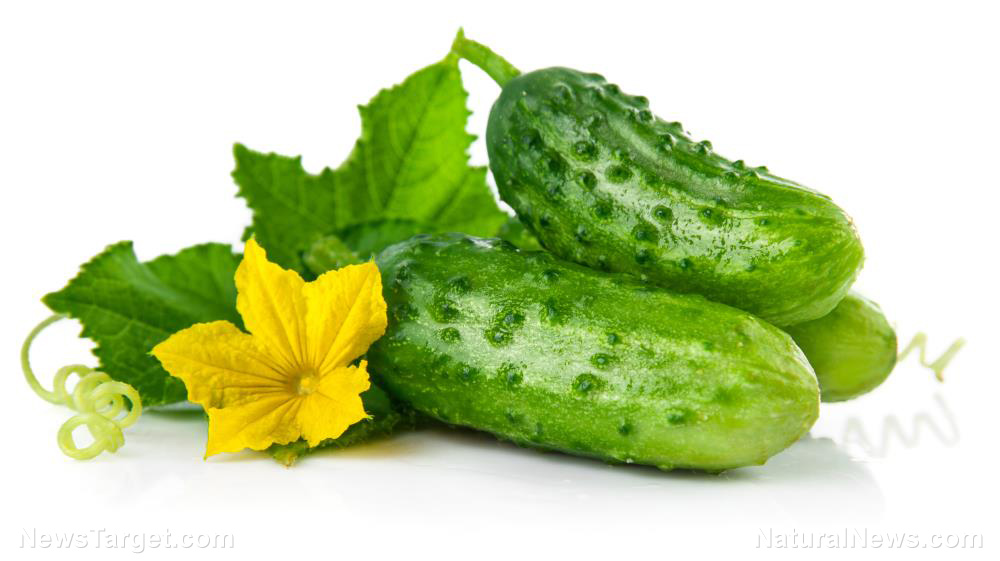

Cucumbers are usually consumed cold or served in salads while zucchinis are often cooked or used for baking. Despite their differences, both plants share some similarities, especially when it comes to their nutritional profiles.
Did you know that zucchini is classified as a vegetable while cucumber is classified as both a fruit and a vegetable?
Nutritional profile
When preparing cucumber and zucchini, leave the peels because they are full of fiber, minerals, and vitamins. Wash both in running water and scrub to remove dirt and residue.
Cucumber and zucchini have similar caloric values. One cup of unpeeled and sliced cucumber has 16 calories while the same serving of unpeeled and sliced zucchini has 19 calories.
A cup of cucumber also has:
- 4 g carbohydrates
- 1 g protein
- 0.50 g dietary fiber
- 0.1 g fat
- Vitamin B6 (three percent of the recommended dietary allowance [RDA])
- Vitamin C (Less than five percent of the RDA)
Meanwhile, a cup of zucchini has:
- 4 g carbohydrates
- 1.4 g protein
- 0.4 g fat
- 1 g dietary fiber
- Vitamin B6 (six percent of the RDA)
- Vitamin C (About 27 percent of the RDA for women and 24 percent of the RDA for men.)
Both cucumber and zucchini contain other essential vitamins and minerals like folate, manganese, potassium, riboflavin, and vitamin K. Potassium can reduce your risk of strokes, and it can naturally lower blood pressure.
According to a study published in the Pakistan Journal of Nutrition, cucumber seeds are full of minerals and calcium. (Related: A cucumber a day keeps the heart doctor away.)
Phytonutrient content
Zucchini seeds contain phytonutrients that prevent inflammation and oxidative stress. They are also believed to have antimicrobial and antiparasitic properties. Its skin is full of antioxidants, so don’t peel zucchinis.
Cucumbers also contain phytonutrients like flavonoids, lignans, and triterpenes. On top of that, cucumbers possess anticancer, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. Cucumber seeds and peels contain beta-carotene and fiber that can enhance skin and eye health and boost your immunity.
Water content
A cucumber is about 95 percent water. Zucchini is also hydrating and contains essential electrolytes.
Both vegetables contain water and fiber that can relieve constipation and improve your digestion.
Cucumbers vs. zucchini: Physical differences
Cucumber and zucchini look similar at first glance: both have the same dark green skin and pale, seedy flesh. Both vegetables are long and cylindrical in shape.
However, cucumbers have a waxy and bumpy exterior. They also feel cold to touch. Some types of cucumbers have smooth skin. Cucumbers have small circular scars instead of stems. Cucumbers have firm, crunchy, and moist flesh.
Zucchini has a dry and rough exterior. Other types of zucchini have orange, yellow, or mottled skin. It has a woody stem at the end. Zucchini feels soft when cut and has dry, spongy flesh.
Both cucumber and zucchini have white flesh, but the former has a tint of green in it.
Taste and usage
Cucumber can be eaten raw or cooked. If you eat it raw, it is crunchy, juicy, and cool. After it is cooked, a cucumber wilts but remains crunchy. Small varieties of cucumber are pickled.
Cucumber can be used for canning and pickling. Cucumber salads are usually served at summer parties and cookouts. Additionally, you can add cucumber slices to water for a detox drink.
Zucchini tastes best when cooked. Cooking turns it brown and brings out its sweet flavor. You can roast, steam, or stir fry zucchini. It can also be used to prepare soups. Alternatively, zucchini can be used as a pasta substitute and turned into noodles or baked into crispy chips.
Ultimately, both cucumber and zucchini should be part of a healthy diet.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: courgette, cucumbers, food cures, food is medicine, Fresh, natural health, natural ingredients, organics, prevention, research, vegetables, veggie, Zucchini